دليل تدريبي: إدارة الأصول الثابتة Asset Management في ERPNext (v15)
هذه الصفحة التدريبية تشرح موديول الأصول الثابتة خطوة بخطوة: من تعريف الأصل وتصنيفه وتحديد موقعه، إلى حركات النقل والصيانة وإثبات الإهلاك والتقارير الرئيسية مثل Asset Depreciation Ledger و Asset Depreciations and Balances.
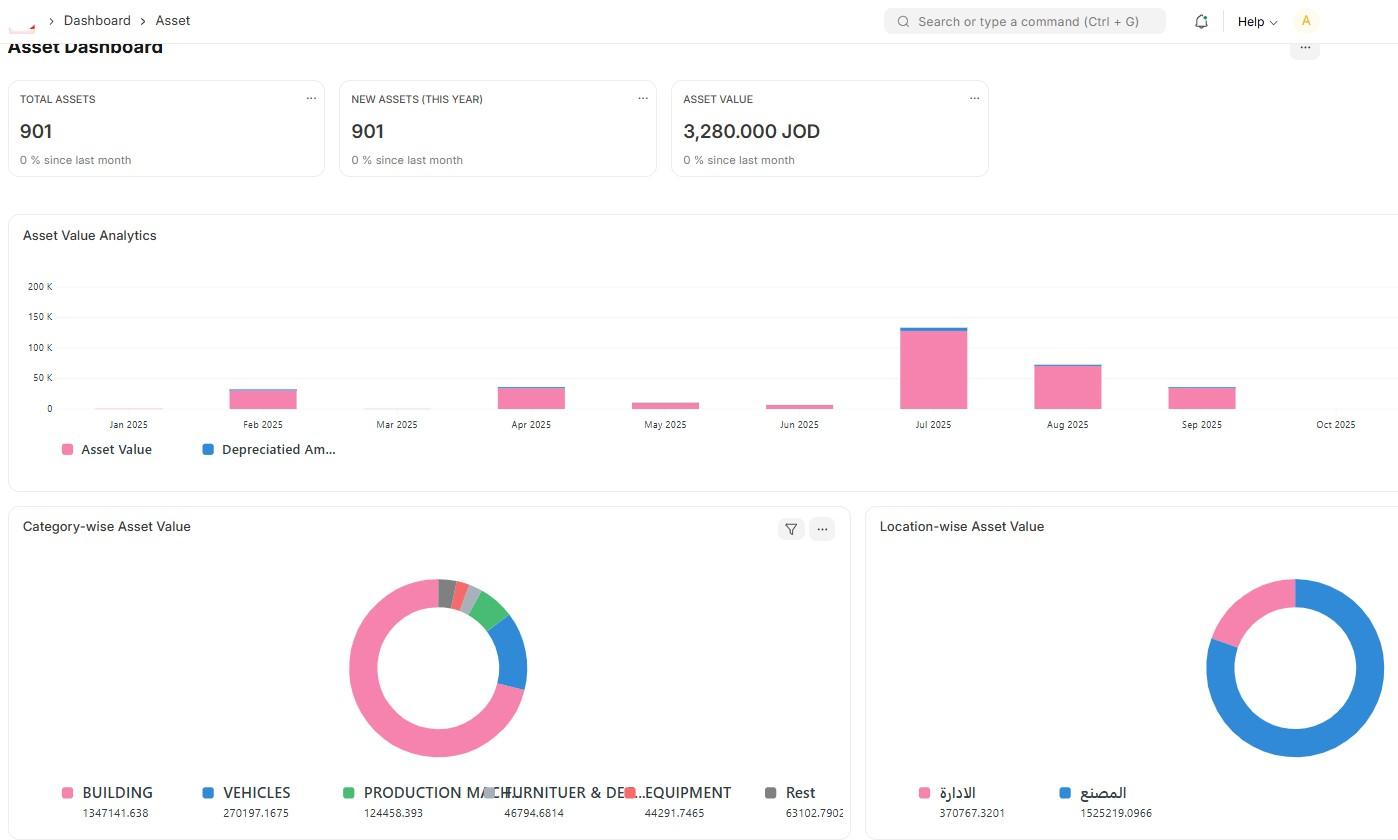
1) ما الذي ستتعلّمه في هذا الموديول؟ (Fixed Asset Overview)
سيركّز هذا الدليل على عناصر الأصول الثابتة الأساسية في ERPNext: Asset، Asset Category، Location، Asset Movement، بالإضافة إلى صيانة الأصول Asset Maintenance / Asset Repair والتسويات Asset Value Adjustment، ورأسملة المصاريف Asset Capitalization، وأخيرًا التقارير القياسية.
- تكوين شجرة تصنيفات للأصول تضبط سياسات الإهلاك والعمر الإنتاجي لكل فئة.
- تعريف الأصول وربطها بالموقع والقسم والموظف المسؤول وتتبع حالتها (نشِط، مُهلك، مباع...).
- تسجيل حركات نقل الأصول بين المواقع والفروع مع أثرها على التقارير.
- إدارة الصيانة والإصلاح وتسجيل التعديلات على قيمة الأصل واحتساب الإهلاك الآلي.
- استخراج التقارير المحاسبية والتحليلية الخاصة بإهلاك الأصول ونشاطها.
2) Asset Category – تصنيف الأصول وسياسات الإهلاك
الفكرة العامة
Asset Category هو المكان الذي تضبط فيه قواعد المحاسبة للأصول: عمر الأصل، طريقة الإهلاك (خط مستقيم، نسبة ثابتة...)، حسابات دفتر الأستاذ (Asset Account، Accumulated Depreciation، Depreciation Expense)، وحدود رأسملة المصاريف.
الحقول الرئيسية
- Asset Category Name – مثل: أثاث مكتبي، أجهزة حاسوب، سيارات...
- Total Number of Depreciations وFrequency (شهري، سنوي...).
- Depreciation Method – Straight Line أو Written Down Value.
- Accounts – ربط الفئة بحسابات الأصول، الإهلاك المتراكم، ومصروف الإهلاك.
أفضل ممارسة
3) Asset – بطاقة الأصل
تعريف الأصل الثابت
مستند Asset يمثل أصلًا واحدًا أو مجموعة وحدات (Batch) يتم إهلاكها وتتبعها معًا. يمكن إنشاؤه يدويًا أو من خلال Purchase Invoice أو Purchase Receipt.
حقول مهمة في بطاقة الأصل
- Asset Name / Asset Tag – كود الأصل واسمه.
- Asset Category – يحدد قواعد الإهلاك والحسابات.
- Company، Location، Department، Custodian.
- Purchase Date، Gross Purchase Amount، Available for Use Date.
- Next Depreciation Date، Expected Value After Useful Life.
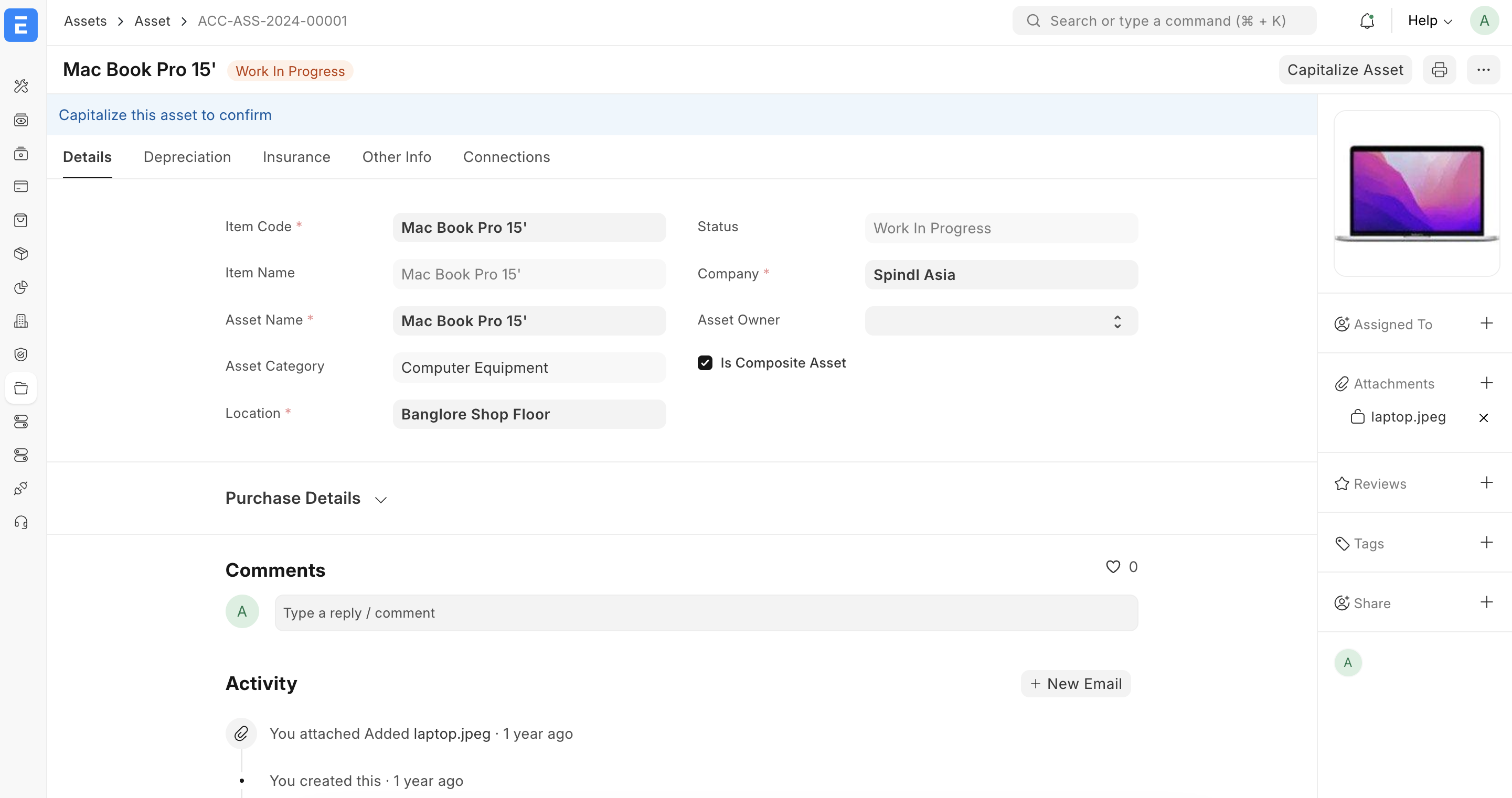
حالات الأصل (Asset Status)
- Draft قبل الاعتماد.
- Submitted أصل معتمد جاهز للإهلاك.
- Partially Depreciated / Fully Depreciated بحسب عدد قيود الإهلاك المنشأة.
- Sold / Scrapped في حال بيع الأصل أو شطبه.
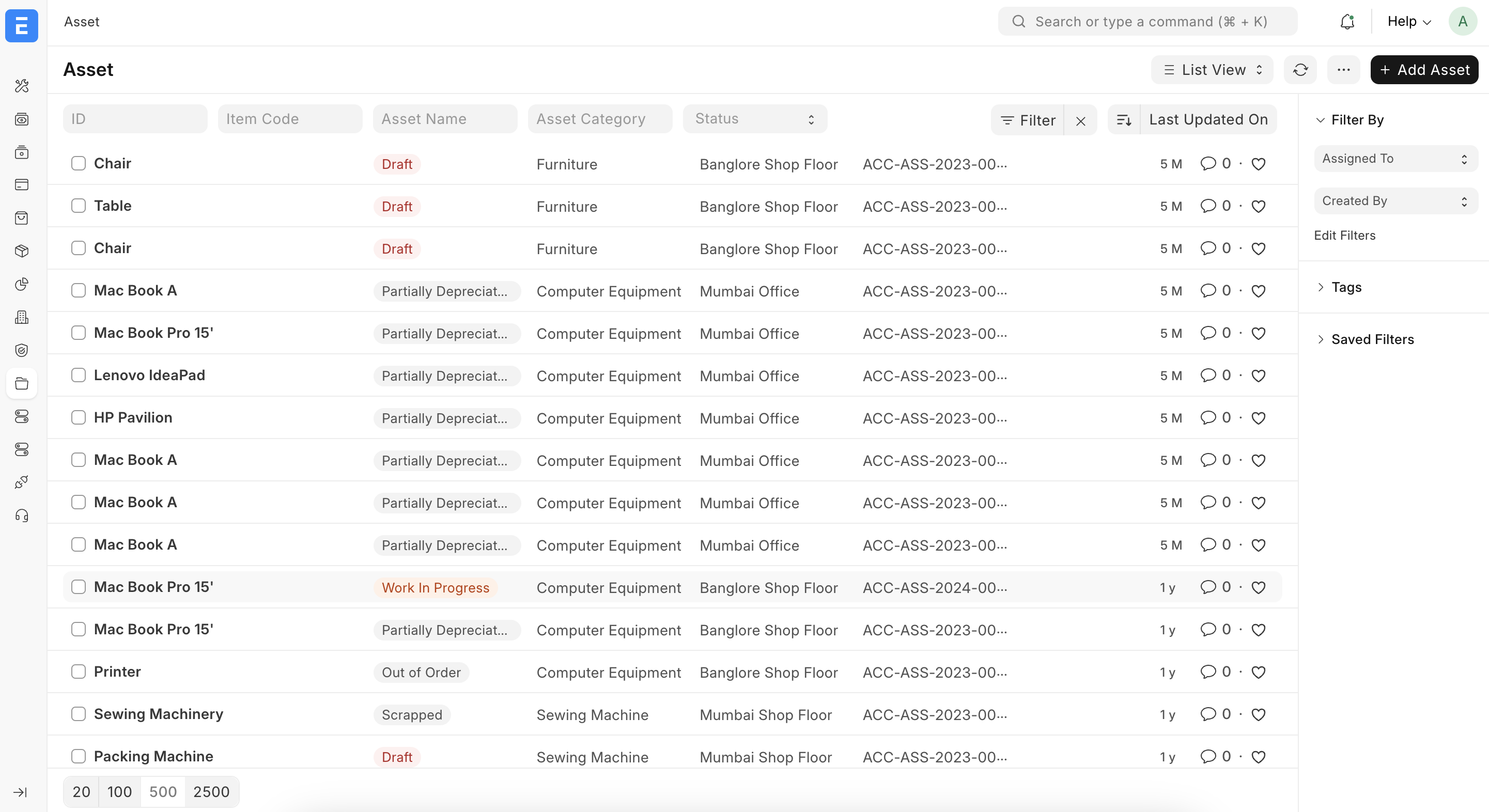
4) Location و Asset Movement – مواقع الأصول وحركاتها
Location – مواقع الأصول
من خلال Location يمكنك إنشاء هيكل المواقع (مبنى، طابق، غرفة، مستودع...) وربط الأصول بكل موقع، مما يسهل الجرد الدوري، وزيارات الصيانة، والتقارير على مستوى الفرع أو المبنى.
Asset Movement – حركة الأصل
مستند Asset Movement يستخدم لتوثيق نقل الأصل بين المواقع أو الأقسام أو حتى نقل مسؤولية العهدة بين الموظفين، مع تسجيل التاريخ والمبرر.
سيناريو تطبيقي
- إنشاء Asset Movement وتحديد الأصل والطرف الناقل والمستلم.
- تغيير Location وDepartment وCustodian في نفس الحركة.
- اعتماد الحركة ليظهر التغيير في التقارير والجرد اللاحق.
5) Maintenance – صيانة الأصول
Asset Maintenance Team
تعريف فرق الصيانة الداخلية أو الخارجية المسؤولة عن متابعة بلاغات الأعطال وجدولة الصيانة الدورية.
Asset Maintenance / Asset Maintenance Log
يمكنك تسجيل خطط الصيانة الدورية (مثل صيانة السيارات كل 10,000 كم أو كل 6 أشهر)، وتوثيق عمليات الصيانة الفعلية في Asset Maintenance Log مع ذكر التاريخ والتكلفة والملاحظات.
Asset Repair
يستخدم Asset Repair لتسجيل عملية إصلاح كبيرة قد تؤثر على Remaining Useful Life أو على Asset Value. يمكن بعد الإصلاح تعديل القيمة من خلال Asset Value Adjustment أو رأسملة المصروف.
6) Asset Value Adjustment & Asset Capitalization – تعديلات القيمة ورأسملة المصاريف
Asset Value Adjustment
يستخدم هذا المستند لتعديل قيمة الأصل (إعادة تقييم، تخفيض قيمة، إضافة تكلفة...) مع توليد القيود المحاسبية المناسبة بين حساب الأصل وحساب التسوية/الفروق.
Asset Capitalization
عندما يكون لديك مصروفات متعلقة بالأصل (مثل تركيب، تحسينات كبيرة على المبنى، تغيير محرك سيارة)، يمكن استخدام Asset Capitalization لنقل المبلغ من حساب المصروف إلى حساب الأصل وزيادة القيمة الدفترية، ثم إعادة احتساب الإهلاك.
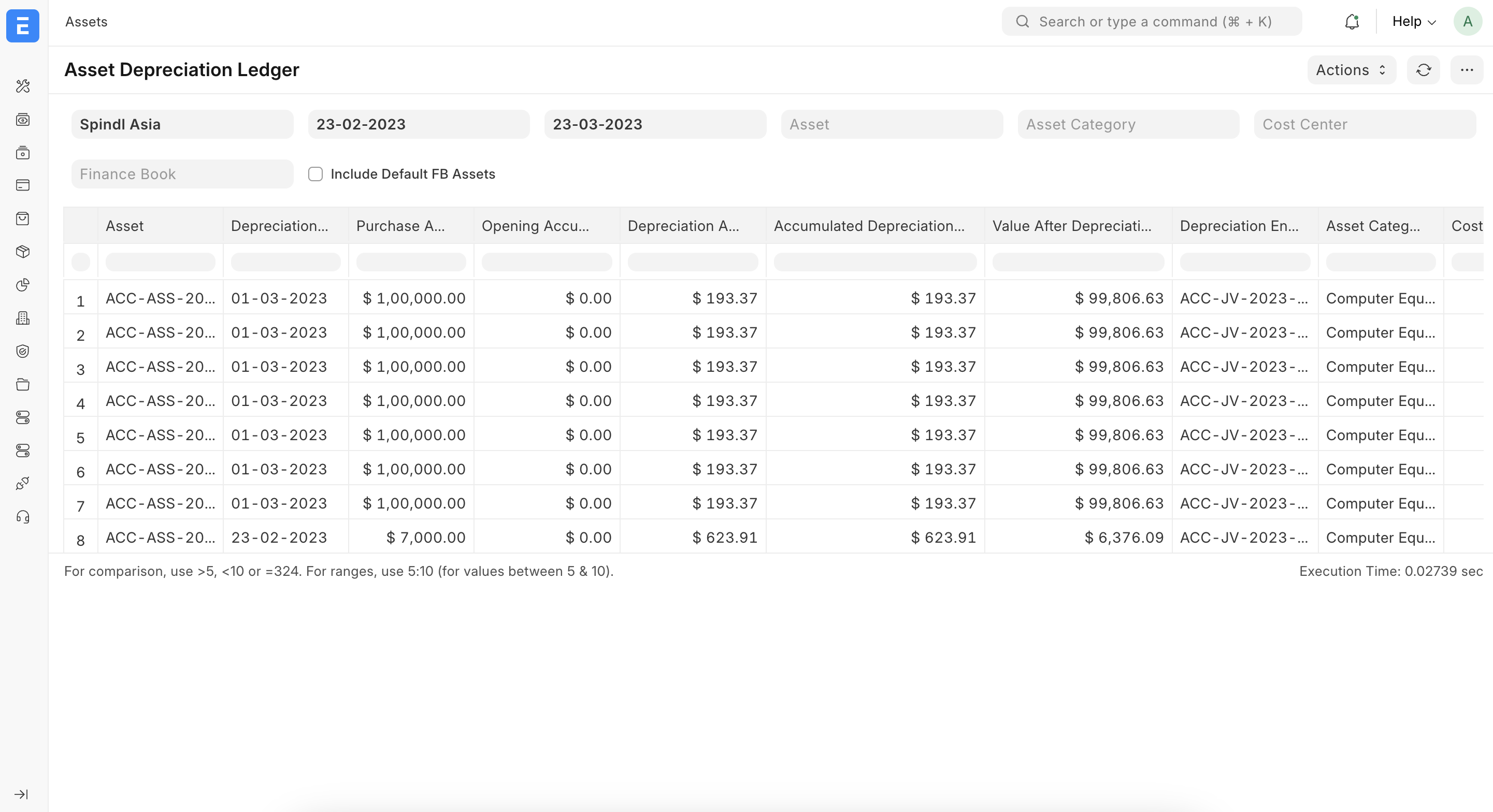
7) Depreciation & Reports – الإهلاك والتقارير
تشغيل الإهلاك
يمكن إنشاء قيود الإهلاك دوريًا باستخدام Asset Depreciation أو من خلال الإجراءات الآلية في النظام. يقوم النظام بإنشاء Journal Entry يحمّل مصروف الإهلاك ويحدّث حساب الإهلاك المتراكم.
التقارير الرئيسية
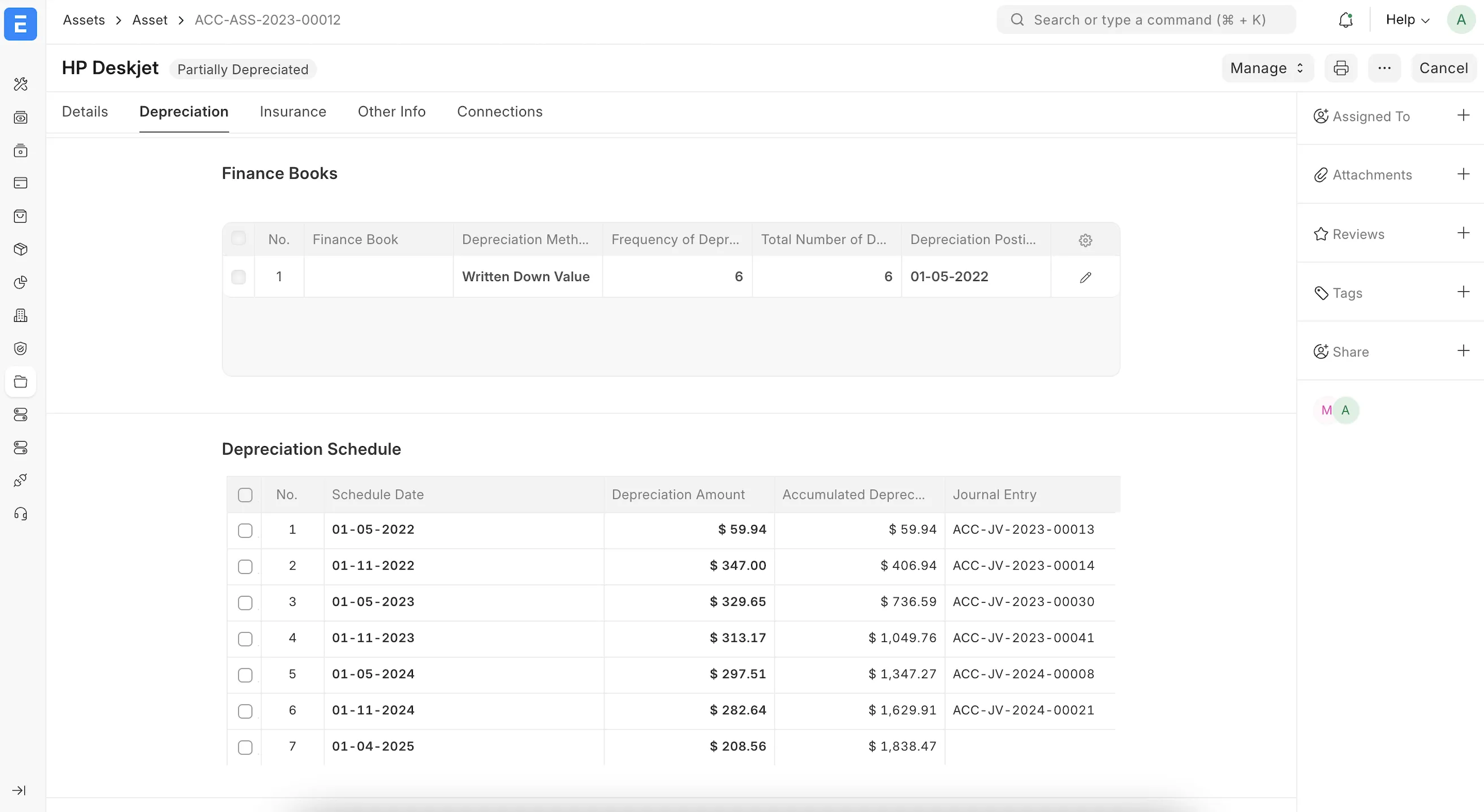
- Asset Depreciation Ledger: يعرض لكل أصل قيود الإهلاك حسب التاريخ والفترة.
- Asset Depreciations and Balances: يوضح القيمة الأصلية، الإهلاك المتراكم، والقيمة الدفترية الصافية لكل أصل أو فئة.
- Asset Maintenance: تقرير عن عمليات الصيانة والتكاليف المرتبطة بكل أصل.
- Asset Activity: ملخص للحركات (شراء، نقل، صيانة، بيع، شطب...).
8) خطة الجلسات التدريبية لموديول الأصول
تسلسل مقترح للتدريب
- شرح مفاهيم الأصول الثابتة المحاسبية وربطها بإعداد Asset Category والحسابات.
- إنشاء مجموعة من الأصول تجريبية من خلال Purchase Invoice ومن خلال الإدخال اليدوي.
- تعريف المواقع Location وتنفيذ أمثلة على Asset Movement.
- إضافة خطة صيانة وتجربة تسجيل صيانة فعلية وإصلاح عبر Asset Maintenance / Asset Repair.
- تشغيل الإهلاك ومراجعة التقارير Asset Depreciation Ledger و Asset Depreciations and Balances.
- تطبيق سيناريو إعادة تقييم أو رأسملة مصاريف وتحليل الأثر على القيمة والإهلاك.
Training Guide: Fixed Asset Management in ERPNext (v15)
This bilingual training page walks you through the fixed asset module in ERPNext: from defining Asset Categories and creating Assets with locations and custodians, to recording Asset Movements, Maintenance, Repairs, value adjustments, and running depreciation reports.
1) What You Will Learn (Fixed Asset Overview)
We will cover the main pieces of the fixed asset module in ERPNext: Asset Category, Asset, Location, Asset Movement, Asset Maintenance, Asset Repair, Asset Value Adjustment, Asset Capitalization, and the key reports such as Asset Depreciation Ledger and Asset Depreciations and Balances.
- Define asset categories with useful life, depreciation method, and GL accounts.
- Create assets from purchase invoices or manually, linking them to locations, departments, and custodians.
- Track movements of assets between branches, buildings, and employees using Asset Movements.
- Manage preventive and corrective maintenance, repairs, and value adjustments.
- Run depreciation and activity reports and reconcile them with the general ledger.

2) Asset Category – Depreciation Rules & Accounts
Concept
Asset Category defines how assets will be depreciated and which accounts are used. Each category can have its own useful life, depreciation frequency and method, and GL mappings.
Key Fields
- Asset Category Name – Office Furniture, Vehicles, IT Equipment, etc.
- Total Number of Depreciations and Frequency (monthly, yearly...).
- Depreciation Method – Straight Line or Written Down Value.
- Accounts – Asset account, accumulated depreciation, and depreciation expense.
3) Asset – Asset Master
Defining Assets
The Asset document represents an individual asset or a batch of identical units. It can be created from a Purchase Invoice / Purchase Receipt or as a manual entry.
Key Fields
- Asset Name / Asset Tag – unique code and descriptive name.
- Asset Category – pulls depreciation rules and accounts.
- Company, Location, Department, Custodian – for responsibility and reporting.
- Purchase Date, Gross Purchase Amount, Available for Use Date.
- Next Depreciation Date, Expected Value After Useful Life.

Asset Status
- Draft – before submission.
- Submitted – active asset, ready for depreciation.
- Partially / Fully Depreciated – based on the posted depreciation entries.
- Sold / Scrapped – once disposal is recorded.
4) Location & Asset Movement
Location
The Location master allows you to build a hierarchy of sites (building, floor, room, warehouse) and assign assets to each node, simplifying physical verification and maintenance visits.
Asset Movement
Asset Movement records transfers of assets between locations, departments, or custodians, keeping a history of who is responsible and where the asset is physically located.
- Create an Asset Movement and select the asset.
- Set source as "Head Office / IT Store" and target as "Head Office / Finance / Employee X".
- Submit the movement so that reports and responsibility reflect the new location and custodian.
5) Maintenance – Asset Maintenance & Repair
Asset Maintenance Team
Define internal or external teams responsible for handling maintenance requests and scheduled services.
Asset Maintenance & Asset Maintenance Log
Use Asset Maintenance to define preventive maintenance plans, and Asset Maintenance Log to record actual services performed with cost, notes, and next service dates.

Asset Repair
For major repairs that can impact asset value or remaining life, use Asset Repair. Afterwards, you may adjust value via Asset Value Adjustment or capitalize the cost.
6) Asset Value Adjustment & Asset Capitalization
Asset Value Adjustment
Use this document to adjust an asset’s book value (revaluation up or down, impairment, corrections). ERPNext will create the appropriate accounting entries between the asset account and the adjustment account.
Asset Capitalization
When you have expenses related to an asset that should be capitalized (e.g. major renovation, engine replacement), Asset Capitalization helps move the cost from an expense account to the asset account, then updates the depreciation base.
7) Depreciation & Reports
Running Depreciation
Depreciation entries can be generated periodically via the Asset Depreciation tools. The system posts Journal Entries that debit depreciation expense and credit accumulated depreciation automatically.
Key Reports
- Asset Depreciation Ledger: shows depreciation entries per asset and period.
- Asset Depreciations and Balances: lists original cost, accumulated depreciation, and net book value for each asset or category.
- Asset Maintenance: summarizes maintenance and repair costs by asset.
- Asset Activity: high-level log of purchases, movements, maintenance, and disposals.

8) Training Session Plan
Suggested order for workshops
- Introduce fixed asset accounting concepts and map them to Asset Category setup.
- Create sample assets from Purchase Invoices and via manual entries.
- Configure Locations and run examples of Asset Movements.
- Define maintenance plans and record actual work using Asset Maintenance and Asset Repair.
- Run depreciation and review Asset Depreciation Ledger and Asset Depreciations and Balances.
- Apply a revaluation or capitalization scenario and analyze the impact on book value and depreciation.